Gas Containing Hydrogen
Decentral Energy Supply with Gas Containing Hydrogen
Gases containing hydrogen include coking gas, coal mine gas, and gases from the gasification of biomass.
These gases have a fluctuating hydrogen content and a relatively low methane (CH4) content, which makes them highly eco-friendly as energy sources. Depending on the gas composition, different MWM gas engine configurations are needed to ensure optimum output and efficiency. Additionally, special safety installations are necessary in order to ensure safe operation with hydrogen. Hydrogen can be used as an energy source for distributed energy generation, as fuel for vehicles, as raw material for chemical processes, and for long-term storage.
Lower Carbon Emissions
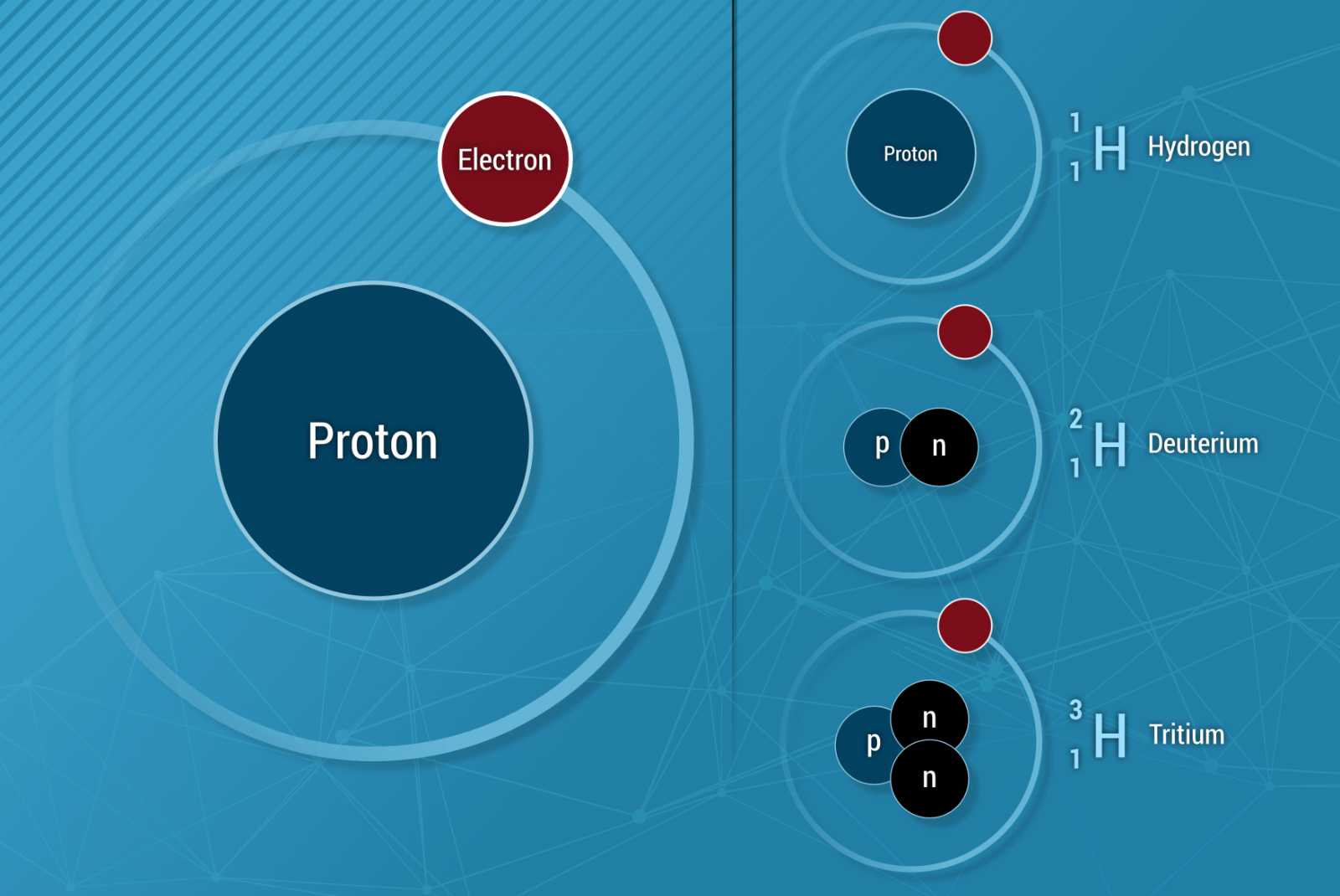
Compared to fossil fuels, the carbon emissions of sustainably and economically produced hydrogen are much lower. Hydrogen is suitable both for centralized and for decentralized power generation. Not all hydrogen types come from zero-carbon production. From the production viewpoint, distinction is made between green, blue, turquoise, and gray hydrogen. About 96 percent of the hydrogen produced around the globe is produced from natural gas, oil, and coal.
Green hydrogen is produced via electrolysis. The power for the electrolysis comes exclusively from renewable energies, e.g. from solar and wind energy or from biomass. The excess energy from the renewable energies is stored with the power-to-X procedure and can be drawn on whenever necessary. The electrolysis splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, using power from sustainable sources. By adding carbon dioxide from the air, hydrogen can be converted either into a climate-neutral fuel gas (power to gas) or into synthetic fuel (power to liquid). Regardless of the electrolysis technology employed, the production of green hydrogen is thus free of carbon emissions, as the utilized power comes exclusively from renewable sources.
Blue hydrogen refers to the hydrogen produced by reforming steam. The resulting CO2 is captured and stored and thus cannot escape into the atmosphere. Accordingly, blue hydrogen boasts a carbon-neutral balance.
Turquoise hydrogen is gained by means of methane pyrolysis, i.e. the thermal splitting of methane. Instead of CO2, this process yields solid carbon.
Gray hydrogen is produced using fossil fuels. In the steam reforming process, natural gas is heated and split into CO2 and hydrogen. The CO2 escapes into the atmosphere.
For a successful energy transition and achievement of the climate targets, the use of green hydrogen as climate-neutral fuel and energy store is a must.
Hydrogen Admixtures in MWM Gas Engines
MWM gas engines are ready for operation with a hydrogen admixture of up to 10 percent. The hydrogen admixture is no problem for the MWM gas engines and can be handled without any technical modifications. Higher hydrogen admixtures of up to 25 percent by volume are also possible, but require technical modification.
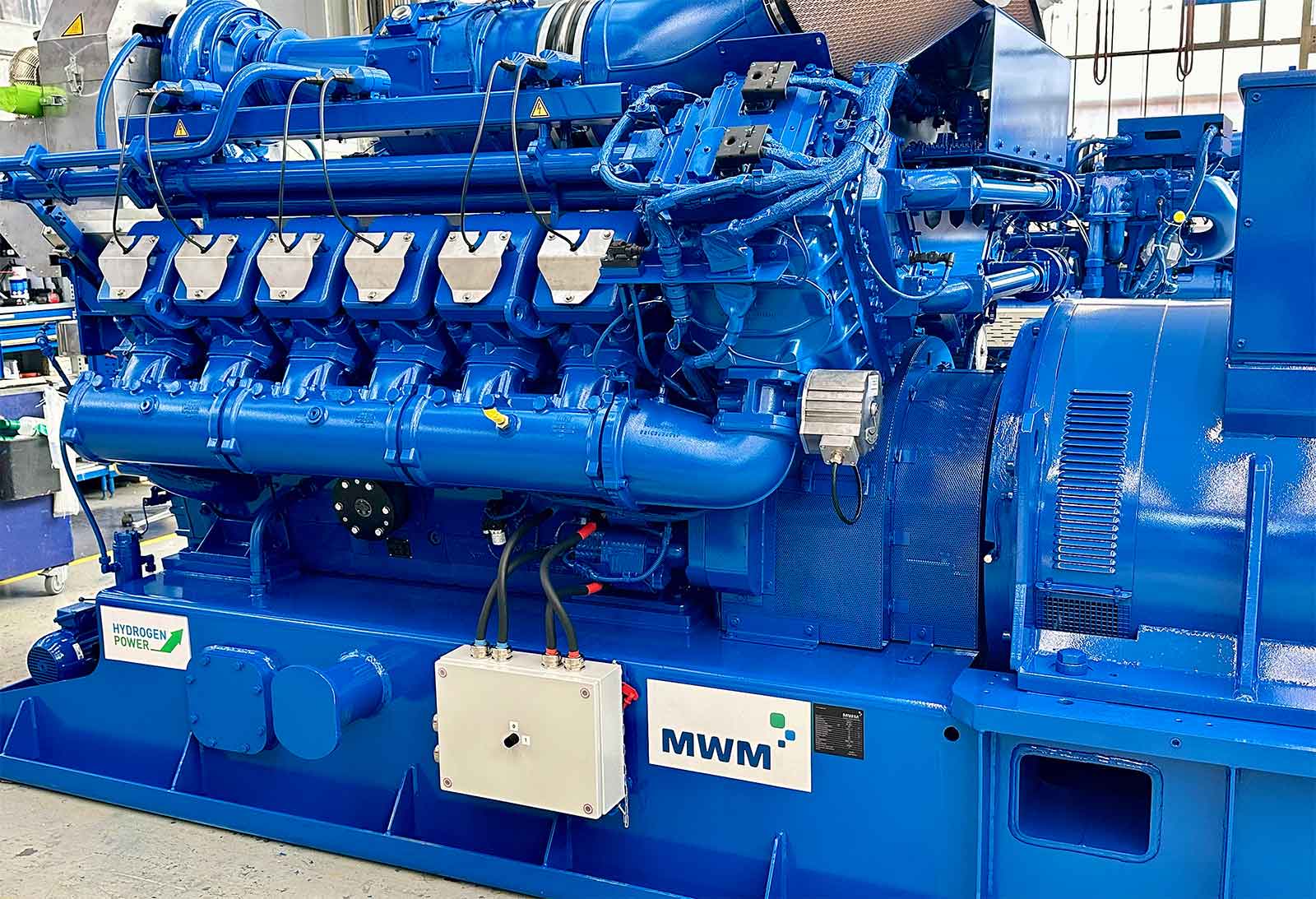

The “Hydrogen Power” signet certifies the operational capability of MWM gas engines with a hydrogen admixture of up to 25 vol%. For existing cogeneration power plants MWM also offers retrofit kits to enable hydrogen admixture. With its range of gas engines that allow an admixture of up to 25% hydrogen by volume, MWM supports plant operators in the gradual switch to more climate-friendly fuels for power and heat production.
Gas engines & Products
Gas Engines / Generator Sets
Gas Engines, gensets, biogas and natural gas generator sets, power generators for decentralized energy supply by MWM, one of the world's leading providers of highly efficient, eco-friendly plants.

Cogeneration Power Plant Solutions
Eco-friendly MWM cogeneration power plants with combined heat and power enable decentralized, economical and energy-efficient power production.